Qt Quick Controls consist of a hierarchy (tree) of items. In order to provide a custom look and feel, the default QML implementation of each item can be replaced with a custom one.
Sometimes you'll want to create a "one-off" look for a specific part of your UI, and use a complete style everywhere else. Perhaps you're happy with the style you're using, but there's a certain button that has some special significance.
The first way to create this button is to simply define it in-place, wherever it is needed. For example, perhaps you're not satisfied with the Basic style's Button having square corners. To make them rounded, you can override the background item and set the radius property of Rectangle:
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ApplicationWindow { width: 400 height: 400 visible: true Button { id: button text: "A Special Button" background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 color: button.down ? "#d6d6d6" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: "#26282a" border.width: 1 radius: 4 } } }
注意: as the different items that make up a control in any given style are designed to work together, it may be necessary to override other items to get the look you're after. In addition, not all styles can be customized. See the note in Customization Reference 了解更多信息。
The second way to create the button is good if you plan to use your rounded button in several places. It involves moving the code into its own QML file within your project.
For this approach, we'll copy the background code from the Basic style's
Button.qml
. This file can be found in the following path in your Qt installation:
$QTDIR/qml/QtQuick/Controls/Basic/Button.qml
After doing that, we'll simply add the following line:
radius: 4
To avoid confusion with the controls in the module itself, we'll call the file
MyButton.qml
. To use the control in your application, refer to it by its filename:
import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ApplicationWindow { MyButton { text: qsTr("A Special Button") } }
The third way to create the button is a bit more structured, both in terms of where the file sits in the file system and how it is used in QML. First, copy an existing file as you did above, but this time, put it into a subfolder in your project named (for example)
controls
. To use the control, first import the folder into a namespace:
import QtQuick.Controls.Basic import "controls" as MyControls ApplicationWindow { MyControls.Button { text: qsTr("A Special Button") } }
As you now have the
MyControls
namespace, you can name the controls after their actual counterparts in the Qt Quick Controls module. You can repeat this process for any control that you wish to add.
An added benefit of these three methods is that it's not necessary to implement the template from scratch.
注意:
the three approaches mentioned here do not work for customizing the attached
ToolTip
, as that is a shared item created internally. To do a one-off customization of a
ToolTip
,见
Custom Tool Tips
. To customize the attached
ToolTip
, it must be provided as part of
your own style
.
There are several ways to go about creating your own styles. Below, we'll explain the various approaches.
In Qt Quick Controls, a style is essentially a set of QML files within a single directory. There are four requirements for a style to be usable :
Button.qml
) must exist.
If we instead used the corresponding type from the QtQuick.Controls import as we did in the previous section, it would not work: the control we were defining would try to derive from itself.
qmldir
file for a style that provides a button:
module MyStyle Button 2.15 Button.qml
若正使用 compile-time style selection , the qmldir should also import the fallback style:
# ... import QtQuick.Controls.Basic auto
This can also be done for run-time style selection instead of using, for example, QQuickStyle::setFallbackStyle ().
The directory structure for such a style looks like this:
MyStyle ├─── Button.qml └─── qmldir
For example, if the path to
MyStyle
directory mentioned above was
/home/user/MyApp/MyStyle
,那么
/home/user/MyApp
must be added to the QML import path.
To 使用 MyStyle in MyApp , refer to it by name:
./MyApp -style MyStyle
The style name must match the casing of the style directory; passing mystyle or MYSTYLE 不支持。
By default, the styling system uses the Basic style as a fallback for controls that aren't implemented. To customize or extend any other built-in style, it is possible to specify a different fallback style using QQuickStyle .
What this means is that you can implement as many controls as you like for your custom style, and place them almost anywhere. It also allows users to create their own styles for your application.
Using the approach above, it is possible to preview a custom style in Qt Quick Designer. In order to do so, ensure that the project has a qtquickcontrols2.conf file, and that the following entry exists:
[Controls] Style=MyStyle
For more information, take a look at the Flat Style example .
Sometimes you may need to use C++ to extend your custom style.
qt_add_qml_module(ACoolItem
URI MyItems
VERSION 1.0
SOURCES
acoolcppitem.cpp acoolcppitem.h
)
CONFIG += qmltypes QML_IMPORT_NAME = MyItems QML_IMPORT_MAJOR_VERSION = 1
If the header the class is declared in is not accessible from your project's include path, you may have to amend the include path so that the generated registration code can be compiled.
INCLUDEPATH += MyItems
见 从 C++ 定义 QML 类型 and 构建 QML 应用程序 了解更多信息。
When implementing your own style and customizing controls, there are some points to keep in mind to ensure that your application is as performant as possible.
As explained in
Definition of a Style
, when you implement your own style for a control, you start off with the relevant template for that control. For example, a style's
Button.qml
will be structured similarly to this:
T.Button { // ... background: Rectangle { // ... } contentItem: Text { // ... } // ... }
When you use a Button in your application, the
background
and
contentItem
items will be created and parented to the root
Button
item:
// Creates the Button root item, the Rectangle background, // and the Text contentItem. Button { text: qsTr("Confirm") }
Suppose you then needed to do a one-off customization of the Button (as explained in Customizing a Control ):
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ApplicationWindow { width: 400 height: 400 visible: true Button { id: button text: "A Special Button" background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 color: button.down ? "#d6d6d6" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: "#26282a" border.width: 1 radius: 4 } } }
In QML, this would normally result in both the default
background
implementation and the one-off, custom
background
items being created. Qt Quick Controls uses a technique that avoids creating both items, and instead only creates the custom
background
, greatly improving the creation performance of controls.
This technique relies on the absence of an
id
in the style's implementation of that item. If an id is assigned, the technique cannot work, and both items will be created. For example, it can be tempting to assign an id to the
background
or
contentItem
so that other objects within the file can refer to those items:
T.Button { // ... background: Rectangle { id: backgroundRect // ... } contentItem: Text { // Use backgroundRect in some way... } // ... }
With this code, every time a Button instance with a customized background is created, both backgrounds will be created, resulting in sub-optimal creation performance.
Prior to Qt 5.15, the old, unused background would be deleted to release the resources associated with it. However, as the control does not own the items, it should not delete them. As of Qt 5.15, old items are no longer deleted, and so the
backgroundRect
item will live longer than it needs to—typically until the application exits. Although the old item will be hidden, visually unparented from the control, and removed from the accessibility tree, it is important to keep the creation time and memory usage of these unused items in mind when assigning an id in this context.
The technique mentioned in the section above only works when an item is declaratively assigned for the first time, and so imperative assignments will result in orphaned items. Always use declarative bindings to assign custom items when possible.
When writing the QML for your style's implementation of a control, it's important not to import
QtQuick.Controls
. Doing so will prevent the QML from being compiled by the QML compiler.
Suppose you were using ScrollViews in your application, and decided that you want to customize their scroll bars. It is tempting to just implement a custom ScrollBar .qml and have ScrollView pick up the customized ScrollBar automatically. However, this will not work. You must implement both ScrollBar .qml and ScrollView .qml.
It is common for a style to have certain properties or attributes that apply to all controls. Attached properties are a great way of extending an item in QML without having to modify any existing C++ belonging to that item. For example, both the Material and Universal styles have an attached theme property that controls whether an item and its children will be rendered in a light or dark theme.
As an example, let's add an attached property that controls elevation. Our style will illustrate the elevation with a drop shadow; the higher the elevation, the larger the shadow.
The first step is to
create a new Qt Quick Controls application
in Qt Creator. After that, we add a C++ type that stores the elevation. Since the type will be used for every control supported by our style, and because we may wish to add other attached properties later on, we'll call it MyStyle. Here is
MyStyle.h
:
#ifndef MYSTYLE_H #define MYSTYLE_H #include <QObject> #include <QtQml> class MyStyle : public QObject { Q_OBJECT Q_PROPERTY(int elevation READ elevation WRITE setElevation NOTIFY elevationChanged) public: explicit MyStyle(QObject *parent = nullptr); static MyStyle *qmlAttachedProperties(QObject *object); int elevation() const; void setElevation(int elevation); signals: void elevationChanged(); private: int m_elevation; }; QML_DECLARE_TYPEINFO(MyStyle, QML_HAS_ATTACHED_PROPERTIES) #endif // MYSTYLE_H
MyStyle.cpp
:
#include "mystyle.h" MyStyle::MyStyle(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent), m_elevation(0) { } MyStyle *MyStyle::qmlAttachedProperties(QObject *object) { return new MyStyle(object); } int MyStyle::elevation() const { return m_elevation; } void MyStyle::setElevation(int elevation) { if (elevation == m_elevation) return; m_elevation = elevation; emit elevationChanged(); }
The
MyStyle
type is special in the sense that it shouldn't be instantiated, but rather used for its attached properties. For that reason, we register it in the following manner in
main.cpp
:
#include <QGuiApplication> #include <QQmlApplicationEngine> #include "mystyle.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QGuiApplication app(argc, argv); qmlRegisterUncreatableType<MyStyle>("MyStyle", 1, 0, "MyStyle", "MyStyle is an attached property"); QQmlApplicationEngine engine; // Make the directory containing our style known to the QML engine. engine.addImportPath(":/"); engine.load(QUrl(QLatin1String("qrc:/main.qml"))); return app.exec(); }
We then copy
Button.qml
from the Basic style in
$QTDIR/qml/QtQuick/Controls/Basic/
into a new
myproject
folder in our project directory. Add the newly copied
Button.qml
to
qml.qrc
, which is the resource file that contains our QML files.
Next, we add a drop shadow to the background delegate of the Button:
// ...
import QtQuick.Effects
import MyStyle
// ...
background: Rectangle {
// ...
layer.enabled: control.enabled && control.MyStyle.elevation > 0
layer.effect: MultiEffect {
shadowEnabled: true
shadowHorizontalOffset: 3
shadowVerticalOffset: 3
shadowColor: control.visualFocus ? "#330066ff" : "#aaaaaa"
shadowBlur: control.pressed ? 0.8 : 0.4
}
}
Note that we:
0
To try out the attached property, we create a
Row
with two Buttons in
main.qml
:
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls import MyStyle 1.0 ApplicationWindow { id: window width: 400 height: 400 visible: true Row { spacing: 20 anchors.centerIn: parent Button { text: "Button 1" } Button { text: "Button 2" MyStyle.elevation: 10 } } }
One button has no elevation, and the other has an elevation of
10
.
With that in place, we can run our example. To tell the application to use our new style, we pass
-style MyStyle
as an application argument, but there are
many ways
to specify the style to use.
The end result:

注意,
import MyStyle 1.0
statement is only necessary because we are using the attached property belonging to
MyStyle
. Both buttons will use our custom style, even if we were to remove the import.
The following snippets present examples where the Basic style's controls have been customized using the same approach as the Customizing a Control section. The code can be used as a starting point to implement a custom look and feel.
注意: The macOS and Windows styles are not suitable for customizing. It is instead recommended to always base a customized control on top of a single style that is available on all platforms, e.g 基本风格 , Fusion 风格 , 想象风格 , 材质风格 , 通用风格 . By doing so, you are guaranteed that it will always look the same, regardless of which style the application is run with. To learn how to use a different style, see 在 Qt Quick Controls 中使用风格 . Alternatively, you can create your own style .
ApplicationWindow consists of one visual item: background .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ApplicationWindow { visible: true background: Rectangle { gradient: Gradient { GradientStop { position: 0; color: "#ffffff" } GradientStop { position: 1; color: "#c1bbf9" } } } }
BusyIndicator consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic BusyIndicator { id: control contentItem: Item { implicitWidth: 64 implicitHeight: 64 Item { id: item x: parent.width / 2 - 32 y: parent.height / 2 - 32 width: 64 height: 64 opacity: control.running ? 1 : 0 Behavior on opacity { OpacityAnimator { duration: 250 } } RotationAnimator { target: item running: control.visible && control.running from: 0 to: 360 loops: Animation.Infinite duration: 1250 } Repeater { id: repeater model: 6 Rectangle { id: delegate x: item.width / 2 - width / 2 y: item.height / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 10 implicitHeight: 10 radius: 5 color: "#21be2b" required property int index transform: [ Translate { y: -Math.min(item.width, item.height) * 0.5 + 5 }, Rotation { angle: delegate.index / repeater.count * 360 origin.x: 5 origin.y: 5 } ] } } } } }
Button consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Button { id: control text: qsTr("Button") contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 border.color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" border.width: 1 radius: 2 } }
CheckBox consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic CheckBox { id: control text: qsTr("CheckBox") checked: true indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.leftPadding y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2 radius: 3 border.color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" Rectangle { width: 14 height: 14 x: 6 y: 6 radius: 2 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" visible: control.checked } } contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter leftPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing } }
CheckDelegate consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic CheckDelegate { id: control text: qsTr("CheckDelegate") checked: true contentItem: Text { rightPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.width - width - control.rightPadding y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 radius: 3 color: "transparent" border.color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" Rectangle { width: 14 height: 14 x: 6 y: 6 radius: 2 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" visible: control.checked } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 visible: control.down || control.highlighted color: control.down ? "#bdbebf" : "#eeeeee" } }
ComboBox consists of background , contentItem , popup , indicator ,和 delegate .

pragma ComponentBehavior: Bound import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ComboBox { id: control model: ["First", "Second", "Third"] delegate: ItemDelegate { id: delegate required property var model required property int index width: control.width contentItem: Text { text: delegate.model[control.textRole] color: "#21be2b" font: control.font elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } highlighted: control.highlightedIndex === index } indicator: Canvas { id: canvas x: control.width - width - control.rightPadding y: control.topPadding + (control.availableHeight - height) / 2 width: 12 height: 8 contextType: "2d" Connections { target: control function onPressedChanged() { canvas.requestPaint(); } } onPaint: { context.reset(); context.moveTo(0, 0); context.lineTo(width, 0); context.lineTo(width / 2, height); context.closePath(); context.fillStyle = control.pressed ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b"; context.fill(); } } contentItem: Text { leftPadding: 0 rightPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing text: control.displayText font: control.font color: control.pressed ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 120 implicitHeight: 40 border.color: control.pressed ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" border.width: control.visualFocus ? 2 : 1 radius: 2 } popup: Popup { y: control.height - 1 width: control.width height: Math.min(contentItem.implicitHeight, control.Window.height - topMargin - bottomMargin) padding: 1 contentItem: ListView { clip: true implicitHeight: contentHeight model: control.popup.visible ? control.delegateModel : null currentIndex: control.highlightedIndex ScrollIndicator.vertical: ScrollIndicator { } } background: Rectangle { border.color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } } }
As explained in ComboBox Model Roles , ComboBox supports multiple types of models.
由于
all the models provide an anonymous property
with
modelData
, the following expression retrieves the right text in all cases:
text: model[control.textRole]
When you provide a specific
textRole
and a model with structured data that provides the selected role, this is expression is a regular property lookup. When you provide a model with singular data, such as a list of strings, and an empty
textRole
, this expression retrieves the
modelData
.
DelayButton consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic DelayButton { id: control checked: true text: qsTr("Delay\nButton") contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: "white" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 100 opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" radius: size / 2 readonly property real size: Math.min(control.width, control.height) width: size height: size anchors.centerIn: parent Canvas { id: canvas anchors.fill: parent Connections { target: control function onProgressChanged() { canvas.requestPaint(); } } onPaint: { var ctx = getContext("2d") ctx.clearRect(0, 0, width, height) ctx.strokeStyle = "white" ctx.lineWidth = parent.size / 20 ctx.beginPath() var startAngle = Math.PI / 5 * 3 var endAngle = startAngle + control.progress * Math.PI / 5 * 9 ctx.arc(width / 2, height / 2, width / 2 - ctx.lineWidth / 2 - 2, startAngle, endAngle) ctx.stroke() } } } }
Dial consists of two visual items: background and handle .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Dial { id: control background: Rectangle { x: control.width / 2 - width / 2 y: control.height / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 140 implicitHeight: 140 width: Math.max(64, Math.min(control.width, control.height)) height: width color: "transparent" radius: width / 2 border.color: control.pressed ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" opacity: control.enabled ? 1 : 0.3 } handle: Rectangle { id: handleItem x: control.background.x + control.background.width / 2 - width / 2 y: control.background.y + control.background.height / 2 - height / 2 width: 16 height: 16 color: control.pressed ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" radius: 8 antialiasing: true opacity: control.enabled ? 1 : 0.3 transform: [ Translate { y: -Math.min(control.background.width, control.background.height) * 0.4 + handleItem.height / 2 }, Rotation { angle: control.angle origin.x: handleItem.width / 2 origin.y: handleItem.height / 2 } ] } }
Drawer can have a visual background 项。
background: Rectangle {
Rectangle {
x: parent.width - 1
width: 1
height: parent.height
color: "#21be2b"
}
}
Frame consists of one visual item: background .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Frame { background: Rectangle { color: "transparent" border.color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } Label { text: qsTr("Content goes here!") } }
GroupBox consists of two visual items: background and label .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic GroupBox { id: control title: qsTr("GroupBox") background: Rectangle { y: control.topPadding - control.bottomPadding width: parent.width height: parent.height - control.topPadding + control.bottomPadding color: "transparent" border.color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } label: Label { x: control.leftPadding width: control.availableWidth text: control.title color: "#21be2b" elide: Text.ElideRight } Label { text: qsTr("Content goes here!") } }
ItemDelegate consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ItemDelegate { id: control text: qsTr("ItemDelegate") contentItem: Text { rightPadding: control.spacing text: control.text font: control.font color: control.enabled ? (control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b") : "#bdbebf" elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#dddedf" : "#eeeeee" Rectangle { width: parent.width height: 1 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" anchors.bottom: parent.bottom } } }
Label can have a visual background 项。

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Label { text: qsTr("Label") color: "#21be2b" }
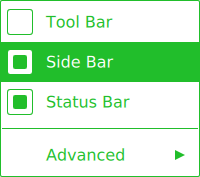
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Menu { id: menu Action { text: qsTr("Tool Bar"); checkable: true } Action { text: qsTr("Side Bar"); checkable: true; checked: true } Action { text: qsTr("Status Bar"); checkable: true; checked: true } MenuSeparator { contentItem: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 1 color: "#21be2b" } } Menu { title: qsTr("Advanced") // ... } topPadding: 2 bottomPadding: 2 delegate: MenuItem { id: menuItem implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 40 arrow: Canvas { x: parent.width - width implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 visible: menuItem.subMenu onPaint: { var ctx = getContext("2d") ctx.fillStyle = menuItem.highlighted ? "#ffffff" : "#21be2b" ctx.moveTo(15, 15) ctx.lineTo(width - 15, height / 2) ctx.lineTo(15, height - 15) ctx.closePath() ctx.fill() } } indicator: Item { implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 Rectangle { width: 26 height: 26 anchors.centerIn: parent visible: menuItem.checkable border.color: "#21be2b" radius: 3 Rectangle { width: 14 height: 14 anchors.centerIn: parent visible: menuItem.checked color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } } } contentItem: Text { leftPadding: menuItem.indicator.width rightPadding: menuItem.arrow.width text: menuItem.text font: menuItem.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: menuItem.highlighted ? "#ffffff" : "#21be2b" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignLeft verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 40 opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 color: menuItem.highlighted ? "#21be2b" : "transparent" } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 40 color: "#ffffff" border.color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } }
MenuBar can have a visual background item, and MenuBarItem consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic MenuBar { id: menuBar Menu { title: qsTr("File") } Menu { title: qsTr("Edit") } Menu { title: qsTr("View") } Menu { title: qsTr("Help") } delegate: MenuBarItem { id: menuBarItem contentItem: Text { text: menuBarItem.text font: menuBarItem.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: menuBarItem.highlighted ? "#ffffff" : "#21be2b" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignLeft verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 color: menuBarItem.highlighted ? "#21be2b" : "transparent" } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 color: "#ffffff" Rectangle { color: "#21be2b" width: parent.width height: 1 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom } } }
PageIndicator consists of a background , contentItem ,和 delegate .
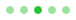
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic PageIndicator { id: control count: 5 currentIndex: 2 delegate: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 8 implicitHeight: 8 radius: width / 2 color: "#21be2b" opacity: index === control.currentIndex ? 0.95 : pressed ? 0.7 : 0.45 required property int index Behavior on opacity { OpacityAnimator { duration: 100 } } } }
Pane consists of a background .
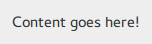
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Pane { background: Rectangle { color: "#eeeeee" } Label { text: qsTr("Content goes here!") } }
Popup consists of a background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Popup { id: popup background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 200 border.color: "#444" } contentItem: Column {} }
ProgressBar consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ProgressBar { id: control value: 0.5 padding: 2 background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 6 color: "#e6e6e6" radius: 3 } contentItem: Item { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 4 // Progress indicator for determinate state. Rectangle { width: control.visualPosition * parent.width height: parent.height radius: 2 color: "#17a81a" visible: !control.indeterminate } // Scrolling animation for indeterminate state. Item { anchors.fill: parent visible: control.indeterminate clip: true Row { spacing: 20 Repeater { model: control.width / 40 + 1 Rectangle { color: "#17a81a" width: 20 height: control.height } } XAnimator on x { from: 0 to: -40 loops: Animation.Infinite running: control.indeterminate } } } } }
Above, the contentItem is also animated to represent an indeterminate progress bar state.
RadioButton consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic RadioButton { id: control text: qsTr("RadioButton") checked: true indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.leftPadding y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2 radius: 13 border.color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" Rectangle { width: 14 height: 14 x: 6 y: 6 radius: 7 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" visible: control.checked } } contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter leftPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing } }
RadioDelegate consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic RadioDelegate { id: control text: qsTr("RadioDelegate") checked: true contentItem: Text { rightPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.width - width - control.rightPadding y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2 radius: 13 color: "transparent" border.color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" Rectangle { width: 14 height: 14 x: 6 y: 6 radius: 7 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" visible: control.checked } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 visible: control.down || control.highlighted color: control.down ? "#bdbebf" : "#eeeeee" } }
RangeSlider consists of three visual items: background , first.handle and second.handle .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic RangeSlider { id: control first.value: 0.25 second.value: 0.75 background: Rectangle { x: control.leftPadding y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 4 width: control.availableWidth height: implicitHeight radius: 2 color: "#bdbebf" Rectangle { x: control.first.visualPosition * parent.width width: control.second.visualPosition * parent.width - x height: parent.height color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } } first.handle: Rectangle { x: control.leftPadding + control.first.visualPosition * (control.availableWidth - width) y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 radius: 13 color: control.first.pressed ? "#f0f0f0" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: "#bdbebf" } second.handle: Rectangle { x: control.leftPadding + control.second.visualPosition * (control.availableWidth - width) y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 radius: 13 color: control.second.pressed ? "#f0f0f0" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: "#bdbebf" } }
RoundButton can be customized in the same manner as Button .
ScrollBar consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ScrollBar { id: control size: 0.3 position: 0.2 active: true orientation: Qt.Vertical contentItem: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 6 implicitHeight: 100 radius: width / 2 color: control.pressed ? "#81e889" : "#c2f4c6" // Hide the ScrollBar when it's not needed. opacity: control.policy === ScrollBar.AlwaysOn || (control.active && control.size < 1.0) ? 0.75 : 0 // Animate the changes in opacity (default duration is 250 ms). Behavior on opacity { NumberAnimation {} } } }
ScrollIndicator consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ScrollIndicator { id: control size: 0.3 position: 0.2 active: true orientation: Qt.Vertical contentItem: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 2 implicitHeight: 100 color: "#c2f4c6" } }
ScrollView consists of a background item, and horizontal and vertical scroll bars.

ScrollView { id: control width: 200 height: 200 focus: true Label { text: "ABC" font.pixelSize: 224 } ScrollBar.vertical: ScrollBar { parent: control x: control.mirrored ? 0 : control.width - width y: control.topPadding height: control.availableHeight active: control.ScrollBar.horizontal.active } ScrollBar.horizontal: ScrollBar { parent: control x: control.leftPadding y: control.height - height width: control.availableWidth active: control.ScrollBar.vertical.active } background: Rectangle { border.color: control.activeFocus ? "#21be2b" : "#bdbebf" } }
Slider consists of two visual items: background ,和 handle .
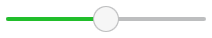
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Slider { id: control value: 0.5 background: Rectangle { x: control.leftPadding y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 4 width: control.availableWidth height: implicitHeight radius: 2 color: "#bdbebf" Rectangle { width: control.visualPosition * parent.width height: parent.height color: "#21be2b" radius: 2 } } handle: Rectangle { x: control.leftPadding + control.visualPosition * (control.availableWidth - width) y: control.topPadding + control.availableHeight / 2 - height / 2 implicitWidth: 26 implicitHeight: 26 radius: 13 color: control.pressed ? "#f0f0f0" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: "#bdbebf" } }
SpinBox consists of four visual items: background , contentItem , up indicator ,和 down indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic SpinBox { id: control value: 50 editable: true contentItem: TextInput { z: 2 text: control.textFromValue(control.value, control.locale) font: control.font color: "#21be2b" selectionColor: "#21be2b" selectedTextColor: "#ffffff" horizontalAlignment: Qt.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Qt.AlignVCenter readOnly: !control.editable validator: control.validator inputMethodHints: Qt.ImhFormattedNumbersOnly } up.indicator: Rectangle { x: control.mirrored ? 0 : parent.width - width height: parent.height implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 color: control.up.pressed ? "#e4e4e4" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: enabled ? "#21be2b" : "#bdbebf" Text { text: "+" font.pixelSize: control.font.pixelSize * 2 color: "#21be2b" anchors.fill: parent fontSizeMode: Text.Fit horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } } down.indicator: Rectangle { x: control.mirrored ? parent.width - width : 0 height: parent.height implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 color: control.down.pressed ? "#e4e4e4" : "#f6f6f6" border.color: enabled ? "#21be2b" : "#bdbebf" Text { text: "-" font.pixelSize: control.font.pixelSize * 2 color: "#21be2b" anchors.fill: parent fontSizeMode: Text.Fit horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 140 border.color: "#bdbebf" } }
SplitView consists of a visual handle delegate.

SplitView { id: splitView anchors.fill: parent handle: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 4 implicitHeight: 4 color: SplitHandle.pressed ? "#81e889" : (SplitHandle.hovered ? Qt.lighter("#c2f4c6", 1.1) : "#c2f4c6") } Rectangle { implicitWidth: 150 color: "#444" } Rectangle { implicitWidth: 50 color: "#666" } }
StackView can have a visual background item, and it allows customizing the transitions that are used for push, pop, and replace operations.
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic StackView { id: control popEnter: Transition { XAnimator { from: (control.mirrored ? -1 : 1) * -control.width to: 0 duration: 400 easing.type: Easing.OutCubic } } popExit: Transition { XAnimator { from: 0 to: (control.mirrored ? -1 : 1) * control.width duration: 400 easing.type: Easing.OutCubic } } }
SwipeDelegate
consists of six visual items:
background
,
contentItem
,
indicator
,
swipe.left
,
swipe.right
,和
swipe.behind
.

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic SwipeDelegate { id: control text: qsTr("SwipeDelegate") Component { id: component Rectangle { color: SwipeDelegate.pressed ? "#333" : "#444" width: parent.width height: parent.height clip: true Label { text: qsTr("Press me!") color: "#21be2b" anchors.centerIn: parent } } } swipe.left: component swipe.right: component contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font color: control.enabled ? (control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b") : "#bdbebf" elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter Behavior on x { enabled: !control.down NumberAnimation { easing.type: Easing.InOutCubic duration: 400 } } } }
SwipeView can have a visual background item. The navigation is implemented by the contentItem .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic SwipeView { id: control background: Rectangle { color: "#eeeeee" } }
Switch consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Switch { id: control text: qsTr("Switch") indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 48 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.leftPadding y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2 radius: 13 color: control.checked ? "#17a81a" : "#ffffff" border.color: control.checked ? "#17a81a" : "#cccccc" Rectangle { x: control.checked ? parent.width - width : 0 width: 26 height: 26 radius: 13 color: control.down ? "#cccccc" : "#ffffff" border.color: control.checked ? (control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b") : "#999999" } } contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter leftPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing } }
SwitchDelegate consists of three visual items: background , contentItem and indicator .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic SwitchDelegate { id: control text: qsTr("SwitchDelegate") checked: true contentItem: Text { rightPadding: control.indicator.width + control.spacing text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" elide: Text.ElideRight verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter } indicator: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 48 implicitHeight: 26 x: control.width - width - control.rightPadding y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2 radius: 13 color: control.checked ? "#17a81a" : "transparent" border.color: control.checked ? "#17a81a" : "#cccccc" Rectangle { x: control.checked ? parent.width - width : 0 width: 26 height: 26 radius: 13 color: control.down ? "#cccccc" : "#ffffff" border.color: control.checked ? (control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b") : "#999999" } } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 100 implicitHeight: 40 visible: control.down || control.highlighted color: control.down ? "#bdbebf" : "#eeeeee" } }
TabBar consists of two visual items: background ,和 contentItem .
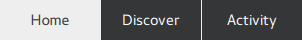
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic TabBar { id: control background: Rectangle { color: "#eeeeee" } TabButton { text: qsTr("Home") } TabButton { text: qsTr("Discover") } TabButton { text: qsTr("Activity") } }
TabButton can be customized in the same manner as Button .
TextArea consists of a background 项。
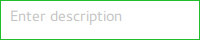
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic TextArea { id: control placeholderText: qsTr("Enter description") background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 40 border.color: control.enabled ? "#21be2b" : "transparent" } }
TextField consists of a background 项。

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic TextField { id: control placeholderText: qsTr("Enter description") background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 200 implicitHeight: 40 color: control.enabled ? "transparent" : "#353637" border.color: control.enabled ? "#21be2b" : "transparent" } }
ToolBar consists of one visual item: background .
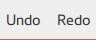
ToolBar { id: control background: Rectangle { implicitHeight: 40 color: "#eeeeee" Rectangle { width: parent.width height: 1 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom color: "transparent" border.color: "#21be2b" } } RowLayout { anchors.fill: parent ToolButton { text: qsTr("Undo") } ToolButton { text: qsTr("Redo") } } }
ToolButton consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ToolButton { id: control text: qsTr("ToolButton") width: 120 contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font opacity: enabled ? 1.0 : 0.3 color: control.down ? "#17a81a" : "#21be2b" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter elide: Text.ElideRight } background: Rectangle { implicitWidth: 40 implicitHeight: 40 color: Qt.darker("#33333333", control.enabled && (control.checked || control.highlighted) ? 1.5 : 1.0) opacity: enabled ? 1 : 0.3 visible: control.down || (control.enabled && (control.checked || control.highlighted)) } }
ToolSeparator consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .

ToolBar { RowLayout { anchors.fill: parent ToolButton { text: qsTr("Action 1") } ToolButton { text: qsTr("Action 2") } ToolSeparator { padding: vertical ? 10 : 2 topPadding: vertical ? 2 : 10 bottomPadding: vertical ? 2 : 10 contentItem: Rectangle { implicitWidth: parent.vertical ? 1 : 24 implicitHeight: parent.vertical ? 24 : 1 color: "#c3c3c3" } } ToolButton { text: qsTr("Action 3") } ToolButton { text: qsTr("Action 4") } Item { Layout.fillWidth: true } } }
ToolTip consists of two visual items: background and contentItem .
import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic ToolTip { id: control text: qsTr("A descriptive tool tip of what the button does") contentItem: Text { text: control.text font: control.font color: "#21be2b" } background: Rectangle { border.color: "#21be2b" } }
注意:
to customize the
attached ToolTip
, it must be provided as part of
your own style
. To do a one-off customization of a
ToolTip
,见
Custom Tool Tips
.
Tumbler consists of three visual items: background , contentItem ,和 delegate .

import QtQuick import QtQuick.Controls.Basic Tumbler { id: control model: 15 background: Item { Rectangle { opacity: control.enabled ? 0.2 : 0.1 border.color: "#000000" width: parent.width height: 1 anchors.top: parent.top } Rectangle { opacity: control.enabled ? 0.2 : 0.1 border.color: "#000000" width: parent.width height: 1 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom } } delegate: Text { text: qsTr("Item %1").arg(modelData + 1) font: control.font horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter opacity: 1.0 - Math.abs(Tumbler.displacement) / (control.visibleItemCount / 2) required property var modelData required property int index } Rectangle { anchors.horizontalCenter: control.horizontalCenter y: control.height * 0.4 width: 40 height: 1 color: "#21be2b" } Rectangle { anchors.horizontalCenter: control.horizontalCenter y: control.height * 0.6 width: 40 height: 1 color: "#21be2b" } }
If you want to define your own contentItem, use either a ListView or PathView as the root item. For a wrapping Tumbler, use PathView :
Tumbler { id: tumbler contentItem: PathView { id: pathView model: tumbler.model delegate: tumbler.delegate clip: true pathItemCount: tumbler.visibleItemCount + 1 preferredHighlightBegin: 0.5 preferredHighlightEnd: 0.5 dragMargin: width / 2 path: Path { startX: pathView.width / 2 startY: -pathView.delegateHeight / 2 PathLine { x: pathView.width / 2 y: pathView.pathItemCount * pathView.delegateHeight - pathView.delegateHeight / 2 } } property real delegateHeight: tumbler.availableHeight / tumbler.visibleItemCount } }
For a non-wrapping Tumbler, use ListView :
Tumbler { id: tumbler contentItem: ListView { model: tumbler.model delegate: tumbler.delegate snapMode: ListView.SnapToItem highlightRangeMode: ListView.StrictlyEnforceRange preferredHighlightBegin: height / 2 - (height / tumbler.visibleItemCount / 2) preferredHighlightEnd: height / 2 + (height / tumbler.visibleItemCount / 2) clip: true } }