SVG 生成器范例展示如何将 SVG 文件导出添加到应用程序。
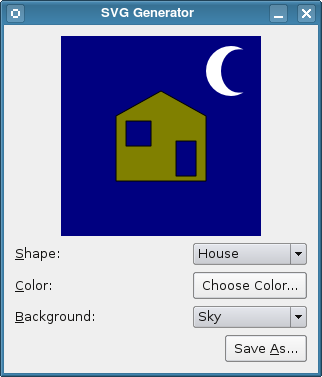
SVG (可伸缩向量图形) 是用于描述 2D 向量图形,基于 XML 的语言。Qt 提供用于渲染和生成 SVG 绘制的类。此范例允许用户创建简单图片并将其保存为 SVG 文件。
范例由 2 个类组成:
Window
and
DisplayWidget
.
Window
class contains the application logic and constructs the user interface from a Qt Designer UI file as described in the
Qt Designer 手册
. It also contains the code to write an SVG file.
DisplayWidget
class performs all the work of painting a picture on screen. Since we want the SVG to resemble this picture as closely as possible, we make this code available to the
Window
class so that it can be used to generate SVG files.
DisplayWidget
class displays a drawing consisting of a selection of elements chosen by the user. These are defined using
形状
and
Background
enums that are included within the class definition:
class DisplayWidget : public QWidget { Q_OBJECT public: enum Shape { House = 0, Car = 1 }; enum Background { Sky = 0, Trees = 1, Road = 2 }; DisplayWidget(QWidget *parent = 0); QColor color() const; void paint(QPainter &painter); public slots: void setBackground(Background background); void setColor(const QColor &color); void setShape(Shape shape); protected: void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) override; private: Background background; QColor shapeColor; Shape shape; QHash<Shape,QPainterPath> shapeMap; QPainterPath moon; QPainterPath tree; };
Much of this class is used to configure the appearance of the drawing. The
paintEvent()
and
paint()
functions are most relevant to the purpose of this example, so we will describe these here and leave the reader to look at the source code for the example to see how shapes and colors are handled.
重实现 QWidget::paintEvent () 函数以在屏幕上显示绘制:
void DisplayWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent * /* event */) { QPainter painter; painter.begin(this); painter.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing); paint(painter); painter.end(); }
Here, we only construct a
QPainter
object, begin painting on the device and set a render hint for improved output quality before calling the
paint()
function to perform the painting itself. When this returns, we close the painter and return.
paint()
function is designed to be used for different painting tasks. In this example, we use it to draw on a
DisplayWidget
instance and on a
QSvgGenerator
object. We show how the painting is performed to demonstrate that there is nothing device-specific about the process:
void DisplayWidget::paint(QPainter &painter) { painter.setClipRect(QRect(0, 0, 200, 200)); painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen); switch (background) { case Sky: default: painter.fillRect(QRect(0, 0, 200, 200), Qt::darkBlue); painter.translate(145, 10); painter.setBrush(Qt::white); painter.drawPath(moon); painter.translate(-145, -10); break; case Trees: { painter.fillRect(QRect(0, 0, 200, 200), Qt::darkGreen); painter.setBrush(Qt::green); painter.setPen(Qt::black); for (int y = -55, row = 0; y < 200; y += 50, ++row) { int xs; if (row == 2 || row == 3) xs = 150; else xs = 50; for (int x = 0; x < 200; x += xs) { painter.save(); painter.translate(x, y); painter.drawPath(tree); painter.restore(); } } break; } case Road: painter.fillRect(QRect(0, 0, 200, 200), Qt::gray); painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::white, 4, Qt::DashLine)); painter.drawLine(QLine(0, 35, 200, 35)); painter.drawLine(QLine(0, 165, 200, 165)); break; } painter.setBrush(shapeColor); painter.setPen(Qt::black); painter.translate(100, 100); painter.drawPath(shapeMap[shape]); }
Window
class represents the example's window, containing the user interface, which has been created using Qt Designer:
class Window : public QWidget, private Ui::Window { Q_OBJECT public: Window(QWidget *parent = 0); public slots: void saveSvg(); void updateBackground(int background); void updateColor(); void updateShape(int shape); private: QString path; };
就像
DisplayWidget
class, we concentrate on the parts of the code which are concerned with painting and SVG generation. In the
Window
class, the
saveSvg()
function is called whenever the
Save As...
button is clicked; this connection was defined in the
window.ui
file using Qt Designer.
The start of the
saveSvg()
function performs the task of showing a file dialog so that the user can specify a SVG file to save the drawing to.
void Window::saveSvg() { QString newPath = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, tr("Save SVG"), path, tr("SVG files (*.svg)")); if (newPath.isEmpty()) return; path = newPath; QSvgGenerator generator; generator.setFileName(path); generator.setSize(QSize(200, 200)); generator.setViewBox(QRect(0, 0, 200, 200)); generator.setTitle(tr("SVG Generator Example Drawing")); generator.setDescription(tr("An SVG drawing created by the SVG Generator " "Example provided with Qt.")); QPainter painter; painter.begin(&generator); displayWidget->paint(painter); painter.end(); }
In the rest of the function, we set up the generator and configure it to generate output with the appropriate dimensions and write to the user-specified file. We paint on the
QSvgGenerator
object in the same way that we paint on a widget, calling the
DisplayWidget::paint()
function so that we use exactly the same code that we used to display the drawing.
The generation process itself begins with the call to the painter's begin() function and ends with call to its end() 函数。 QSvgGenerator paint device relies on the explicit use of these functions to ensure that output is written to the file.
SVG 查看器范例 shows how to display SVG drawings in an application, and can be used to show the contents of SVG files created by this example.
见 Qt SVG 模块文档编制,了解有关 SVG 和 Qt SVG 类的更多信息。