On a device there can be many types of sensors. Not all of the types that the Qt Sensors API supports may be available. There may also be types available that are not defined in the Qt Sensors API. The types of sensors available on a device is found using the QSensor::sensorTypes () 函数。
For a list of built-in sensor types, see the Sensor Classes 以下章节。
Unless specified otherwise, Qt Sensors uses the Right Hand Cartesian coordinate system .
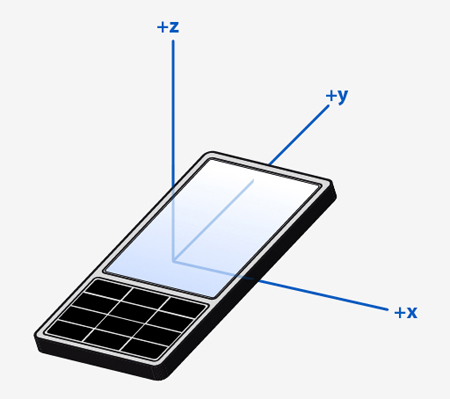
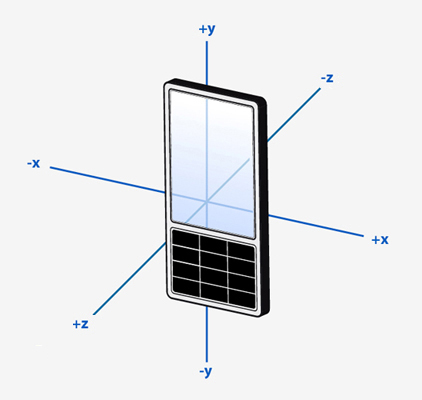
To allow for measurements in all 6 directions, negative values are used.
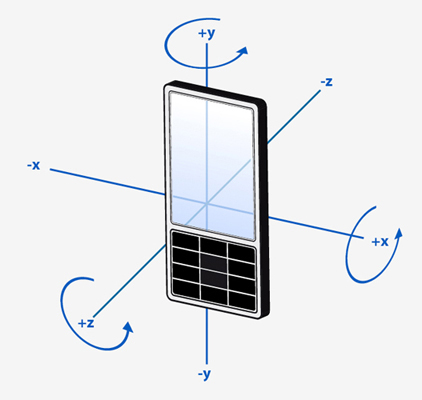
Where rotation around an axis is used, the rotation shall be expressed as a Right Hand rotation.
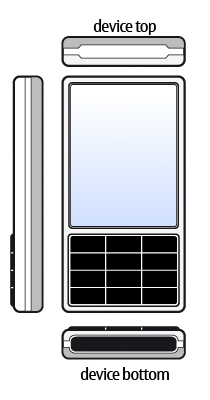
In general, sensor data is oriented relative to QScreen::nativeOrientation , that is to the top of the device when the device is held in its natural orientation (normally when the device logo appears the right side up). If values are to be displayed on the screen, the values may need to be transformed so that they match the user interface orientation. A sensor may define its data as being oriented to the UI. This will be noted in the documentation for the sensor.
The life cycle of a QSensor is typically:
Here is an example of creating a sensor on the heap and on the stack.
// On the heap (deleted when this object is deleted) QAccelerometer *sensor = new QAccelerometer(this); // On the stack (deleted when the current scope ends) QOrientationSensor orient_sensor;
The preferred way to deal with sensor data is via the Reading Classes . However, sometimes this may not be possible. For example, you may be deploying an application to a device that has a new sensor type but no C++ header describing the reading class is available.
Thanks to Qt's property system you can still access the sensor data. You need to know 3 pieces of information in order to do this:
For example, here is an example of how you can access a property of the accelerometer. This code does not require any compile-time links to QAccelerometer or QAccelerometerReading .
// start the sensor QSensor sensor("QAccelerometer"); sensor.start(); // later QSensorReading *reading = sensor.reading(); qreal x = reading->property("x").value<qreal>(); qreal y = reading->value(1).value<qreal>();
You can discover all of this information at runtime too. The sensor_explorer example shows you information about available sensors.
The Qt Sensors API has a front end, for application developers to use and a back end, where device implementors write code to access their hardware. As an application developer you do not need to access the back end though it may be useful to understand how it works.
Commands from the application are delivered through QSensor and then down to the device plugin. Data comes back through the QSensorReading 类。
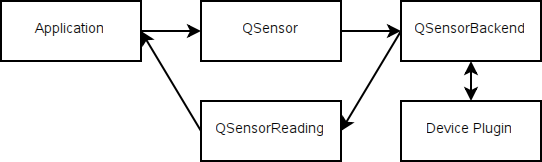
More information about the back end can be found in Qt Sensors Backend .
The primary classes that make up the Qt Sensors API.
| QSensor | Represents a single hardware sensor |
| QSensorFilter | Efficient callback facility for asynchronous notifications of sensor changes |
| QSensorReading | Holds the readings from the sensor |
The best way to access sensor data is via one of these classes.
| QAccelerometerReading | Reports on linear acceleration along the X, Y and Z axes |
| QAmbientLightReading | Represents one reading from the ambient light sensor |
| QAmbientTemperatureReading | Holds readings of the ambient temperature |
| QCompassReading | Represents one reading from a compass |
| QGyroscopeReading | Represents one reading from the gyroscope sensor |
| QHumidityReading | Holds readings from the humidity sensor |
| QLightReading | Represents one reading from the light sensor |
| QMagnetometerReading | Represents one reading from the magnetometer |
| QOrientationReading | Represents one reading from the orientation sensor |
| QPressureReading | Holds readings from the pressure sensor |
| QProximityReading | Represents one reading from the proximity sensor |
| QRotationReading | Represents one reading from the rotation sensor |
| QTiltReading | 保持来自倾斜传感器的读数 |
These classes provide convenience wrappers that reduce the need for casting. Each of these classes represents a sensor type that the Qt Sensors API knows about. Note that additional types may be made available at run-time. See Sensor Types 了解更多信息。
| QAccelerometer | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QAmbientLightSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QAmbientTemperatureSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QCompass | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QGyroscope | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QHumiditySensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QLightSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QMagnetometer | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QOrientationSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QPressureSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QProximitySensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QRotationSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
| QTiltSensor | 围绕 QSensor 的方便包裹器 |
As with the sensor classes, these provide convenience wrappers that reduce the need for casting.
| QAccelerometerFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QAmbientLightFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QAmbientTemperatureFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QCompassFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QGyroscopeFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QHumidityFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QLightFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QMagnetometerFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QOrientationFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QPressureFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QProximityFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QRotationFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |
| QTiltFilter | 围绕 QSensorFilter 的方便包裹器 |