A rich-text editor app using Qt Quick Controls.
The
Text Editor Example
allows WYSIWYG editing of an HTML, Markdown or plain text file. The application comes with two user interfaces: one for larger screens, and a simplified UI for small touch-based devices. Both are "pure" QML.
texteditor.cpp
包含
main()
function, which calls
QFontDatabase::addApplicationFont
() to add an icon font. (
FontLoader
would be an alternative way to achieve the same result.)
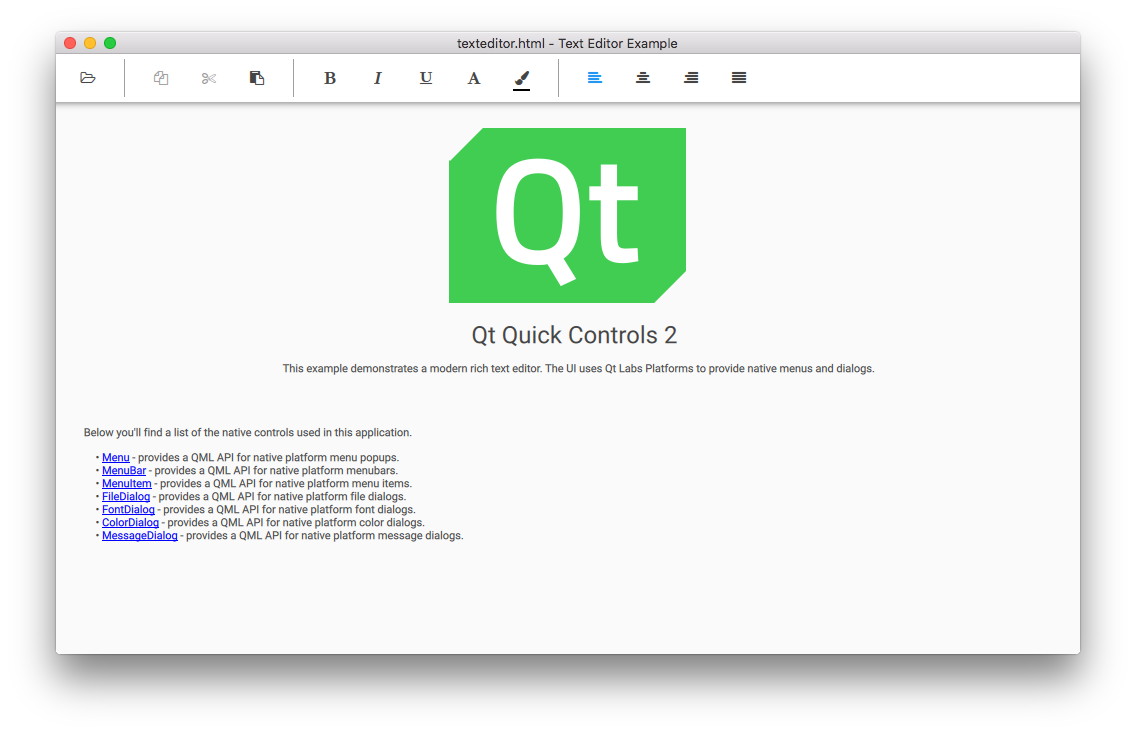
The desktop version is a complete text editor with capabilities for formatting text, and opening and saving HTML, Markdown and plain text files.
在 model-view-control (MVC) design pattern, the control layer includes the set of operations that can be performed. In Qt Quick Controls, the 动作 type is used to encapsulate a single operation or command. Accordingly, we begin with a set of Action objects:
Action {
id: openAction
text: qsTr("&Open")
shortcut: StandardKey.Open
onTriggered: {
if (textArea.textDocument.modified)
discardDialog.open()
else
openDialog.open()
}
}
The 动作 for opening a file must first prompt the user if the existing document has been changed, to avoid losing the user's changes. Otherwise it simply opens the FileDialog which is declared further below.
The 动作 for saving the file is enabled only if there are changes to save:
Action {
id: saveAction
text: qsTr("&Save…")
shortcut: StandardKey.Save
enabled: textArea.textDocument.modified
onTriggered: textArea.textDocument.save()
}
The 动作 for copying selected text is enabled only if some text is selected:
Action {
id: copyAction
text: qsTr("&Copy")
shortcut: StandardKey.Copy
enabled: textArea.selectedText
onTriggered: textArea.copy()
}
Each Action to change text formatting (such as bold, italic and alignment) is
checkable
, and its boolean
checked
state is in sync with the relevant property in the
selected text
. Since declarative bidirectional synchronization is difficult, we use an
onTriggered
script to change the property when the Action is activated. The
cursorSelection
property is new in Qt 6.7 and makes this much easier than it was.
Action {
id: boldAction
text: qsTr("&Bold")
shortcut: StandardKey.Bold
checkable: true
checked: textArea.cursorSelection.font.bold
onTriggered: textArea.cursorSelection.font.bold = checked
}
Action {
id: alignCenterAction
text: qsTr("&Center")
shortcut: "Ctrl+|"
checkable: true
checked: textArea.cursorSelection.alignment === Qt.AlignCenter
onTriggered: textArea.cursorSelection.alignment = Qt.AlignCenter
}
We have a MenuBar containing the hierarchy of 菜单 and MenuItems. Each MenuItem merely needs to bind the relevant action , which encapsulates the UI representation and the implementation.
menuBar: MenuBar {
Menu {
title: qsTr("&File")
MenuItem {
action: openAction
}
MenuItem {
action: saveAction
}
MenuItem {
action: saveAsAction
}
MenuItem {
action: quitAction
}
}
Menu {
title: qsTr("&Edit")
MenuItem {
action: copyAction
}
...
The same 动作 objects are reused in the ToolBar ; but here we override each Action's text property to choose a textual icon from our icon font:
header: ToolBar {
Flow {
width: parent.width
Row {
id: fileRow
ToolButton {
id: openButton
text: "\uF115" // icon-folder-open-empty
font.family: "fontello"
action: openAction
focusPolicy: Qt.TabFocus
}
ToolButton {
id: saveButton
text: "\uE80A" // icon-floppy-disk
font.family: "fontello"
action: saveAction
focusPolicy: Qt.TabFocus
}
ToolSeparator {
contentItem.visible: fileRow.y === editRow.y
}
}
Row {
id: editRow
ToolButton {
id: copyButton
text: "\uF0C5" // icon-docs
font.family: "fontello"
focusPolicy: Qt.TabFocus
action: copyAction
}
...
The main part of the text editor is a TextArea 在 Flickable :
Flickable {
id: flickable
flickableDirection: Flickable.VerticalFlick
anchors.fill: parent
ScrollBar.vertical: ScrollBar {}
TextArea.flickable: TextArea {
id: textArea
textFormat: Qt.AutoText
wrapMode: TextArea.Wrap
focus: true
selectByMouse: true
persistentSelection: true
...
A ScrollBar is attached to the vertical axis. Since word-wrapping is enabled via wrapMode , we don't need a horizontal ScrollBar .
The TextArea.flickable attached property is used so that when the text cursor is moved out of the viewport (for example via arrow keys, or by typing a lot of text), TextArea scrolls the Flickable to keep the cursor visible.
There is a context menu; we use a TapHandler to detect a right-click and open it:
TapHandler {
acceptedButtons: Qt.RightButton
onTapped: contextMenu.popup()
}
The context Menu 包含 MenuItems that reuse the same 动作 objects as the main MenuBar and ToolBar are using. As before, it's enough to bind action to the reusable Action that represents the operation to be performed. However, we override each menu item's text to omit the underlined mnemonics on the context menu.
Menu {
id: contextMenu
MenuItem {
text: qsTr("Copy")
action: copyAction
}
...
We consistently use the qsTr () function to enable translation of UI text, so that the application will make sense regardless of the end user's native language.
We use several kinds of dialogs :
FileDialog {
id: openDialog
fileMode: FileDialog.OpenFile
selectedNameFilter.index: 1
nameFilters: ["Text files (*.txt)", "HTML files (*.html *.htm)", "Markdown files (*.md *.markdown)"]
currentFolder: StandardPaths.writableLocation(StandardPaths.DocumentsLocation)
onAccepted: {
textArea.textDocument.modified = false // we asked earlier, if necessary
textArea.textDocument.source = selectedFile
}
}
FileDialog {
id: saveDialog
fileMode: FileDialog.SaveFile
nameFilters: openDialog.nameFilters
currentFolder: StandardPaths.writableLocation(StandardPaths.DocumentsLocation)
onAccepted: textArea.textDocument.saveAs(selectedFile)
}
FontDialog {
id: fontDialog
onAccepted: textArea.cursorSelection.font = selectedFont
}
ColorDialog {
id: colorDialog
selectedColor: textArea.cursorSelection.color
onAccepted: textArea.cursorSelection.color = selectedColor
}
MessageDialog {
title: qsTr("Error")
id: errorDialog
}
MessageDialog {
id : quitDialog
title: qsTr("Quit?")
text: qsTr("The file has been modified. Quit anyway?")
buttons: MessageDialog.Yes | MessageDialog.No
onButtonClicked: function (button, role) {
if (role === MessageDialog.YesRole) {
textArea.textDocument.modified = false
Qt.quit()
}
}
}
MessageDialog {
id : discardDialog
title: qsTr("Discard changes?")
text: qsTr("The file has been modified. Open a new file anyway?")
buttons: MessageDialog.Yes | MessageDialog.No
onButtonClicked: function (button, role) {
if (role === MessageDialog.YesRole)
openDialog.open()
}
}
It's generally easier to declare separate instances for each purpose. We have two instances of FileDialog , for opening and saving files respectively. This became easier in Qt 6.7, with new features in TextDocument .
A FontDialog 和 ColorDialog allow changing text formatting. (In Markdown format, there's no syntax to represent specific font and color choices; but font characteristics such as bold, italic and monospace are saved. In HTML format, all formatting is saved.)
We have a MessageDialog to show error messages, and two more for prompting the user what to do when a file has been modified.
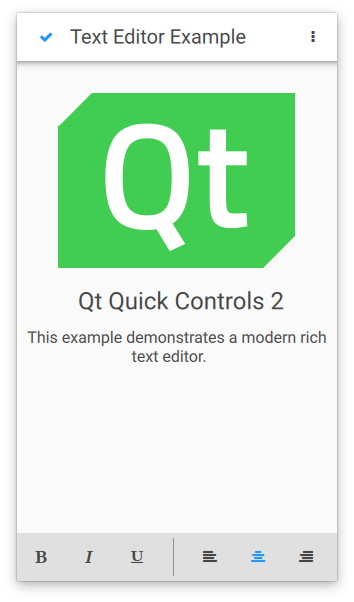
The touch user interface is a simplified version of the text editor. It is suitable for touch devices with limited screen size. The example uses file selectors to load the appropriate user interface automatically.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,见 Qt Creator:教程:构建并运行 .