This example shows the drawing of microphone samples vs audio level.
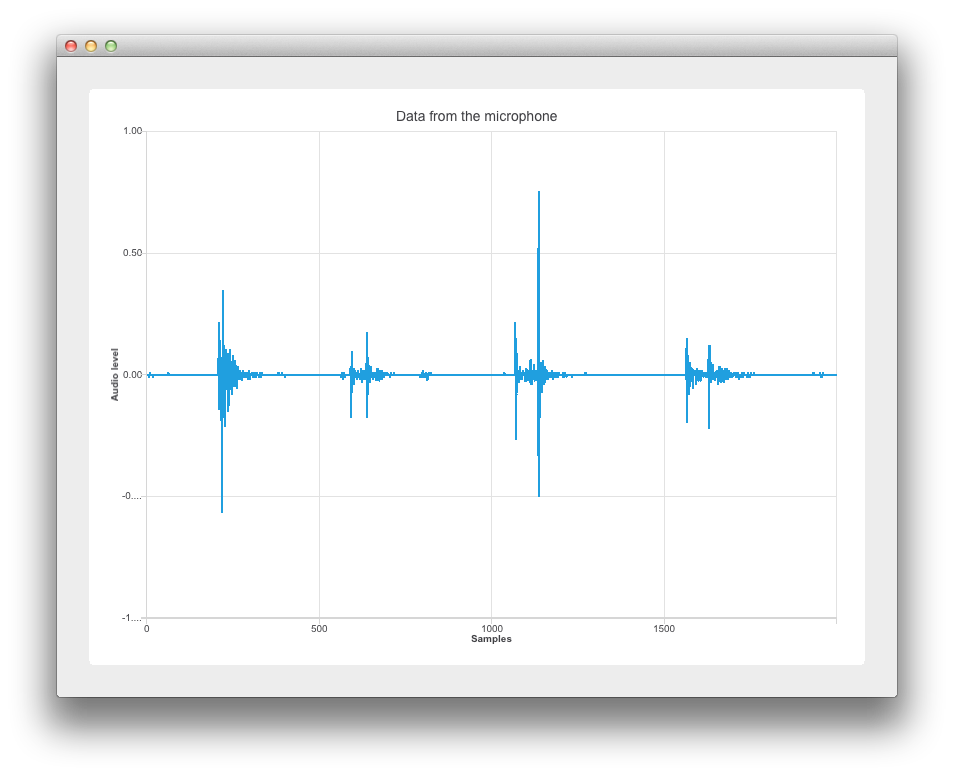
This example's implementation is based on Widgets. See 采用 Qt Widgets 快速入门编程 for information specific to that. The following sections cover how to use the Qt Charts API to display dynamic data on a samples vs sound level graph. For more information on sampling, see Sampling_(signal_processing) .
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
Thanks to the inclusion of the Qt Multimedia module in
main.cpp
, we create a new
QAudioDevice
that represents the default audio device of the target platform. We also check that we have an audio input device and let the user know if there is no input audio device available.
if (inputDevice.isNull()) {
QMessageBox::warning(nullptr, "audio",
"There is no audio input device available.");
return -1;
}
The audio device is then passed to Widget
w
using its constructor argument
w
。然后
w.show()
is called to display the widget.
Widget w(inputDevice);
w.resize(800, 600);
w.show();
This section covers setting up the chart and axes.
在
widget.cpp
, the re-implemented Widget constructor does the heavy lifting when it comes to the application's logic. The
QChart
,
QLineSeries
,和
QChartView
objects are declared as follows:
: QWidget(parent)
, m_chart(new QChart)
, m_series(new QLineSeries)
{
auto chartView = new QChartView(m_chart);
m_chart->addSeries(m_series);
m_series is for Using the audio input data .
We set the min to max range on the x-axis from 0 to the XYSeriesIODevice::sampleCount. (Declared in xyseriesiodevice.h as 2000). We then set its title text.
auto axisX = new QValueAxis;
axisX->setRange(0, XYSeriesIODevice::sampleCount);
axisX->setLabelFormat("%g");
axisX->setTitleText("Samples");
创建
QValueAxis
axisY
, set its range and title text.
auto axisY = new QValueAxis;
axisY->setRange(-1, 1);
axisY->setTitleText("Audio level");
We attach the axes, hide the legend, and set the chart title to include the name of the microphone being used as an audio input.
m_chart->addAxis(axisX, Qt::AlignBottom);
m_series->attachAxis(axisX);
m_chart->addAxis(axisY, Qt::AlignLeft);
m_series->attachAxis(axisY);
m_chart->legend()->hide();
Here we use a
QVBoxLayout
mainLayout
and add a our QChartview
chartView
to the vertical layout.
m_chart->setTitle("Data from the microphone (" + deviceInfo.description() + ')');
auto mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout(this);
This section shows how the microphone data is passed to the
QLineSeries
m_series
. As before this relies on the Qt Multimedia module.
First we pass deviceInfo to a QAudioInput 构造函数。
mainLayout->addWidget(chartView);
m_audioInput = new QAudioInput(deviceInfo, this);
QAudioFormat formatAudio;
We then setup our
QAudioFormat
formatAudio
, its channel count, sample rate, and sample format.
formatAudio.setSampleRate(8000);
formatAudio.setChannelCount(1);
We can now create a QAudioSource and set its buffer size.
formatAudio.setSampleFormat(QAudioFormat::UInt8);
m_audioSource = new QAudioSource(deviceInfo, formatAudio);
Now its time to attach our data to the chart. To do this we have created a class XYSeriesIODevice. See XYSeriesIODevice for how it is implemented.
m_audioSource->setBufferSize(200);
m_device = new XYSeriesIODevice(m_series, this);
m_device->open(QIODevice::WriteOnly);
Implemented in
xyseriesiodevice.cpp
, XYSeriesIODevice takes care of the signal sampling. The
writeData
function, with a fixed resolution of 4, sets the
QList
m_buffer
size based on the sample count, and fills it with QPointFs with an incremental x value and the y value set to 0.
{
static const int resolution = 4;
if (m_buffer.isEmpty()) {
m_buffer.reserve(sampleCount);
for (int i = 0; i < sampleCount; ++i)
m_buffer.append(QPointF(i, 0));
}
int start = 0;
We then do some sampling.
const int availableSamples = int(maxSize) / resolution;
if (availableSamples < sampleCount) {
start = sampleCount - availableSamples;
for (int s = 0; s < start; ++s)
m_buffer[s].setY(m_buffer.at(s + availableSamples).y());
}
for (int s = start; s < sampleCount; ++s, data += resolution)
m_buffer[s].setY(qreal(uchar(*data) -128) / qreal(128));
m_series->replace(m_buffer);
return (sampleCount - start) * resolution;