Demonstrates how to make a simple locomotion in Qt Quick 3D XR.
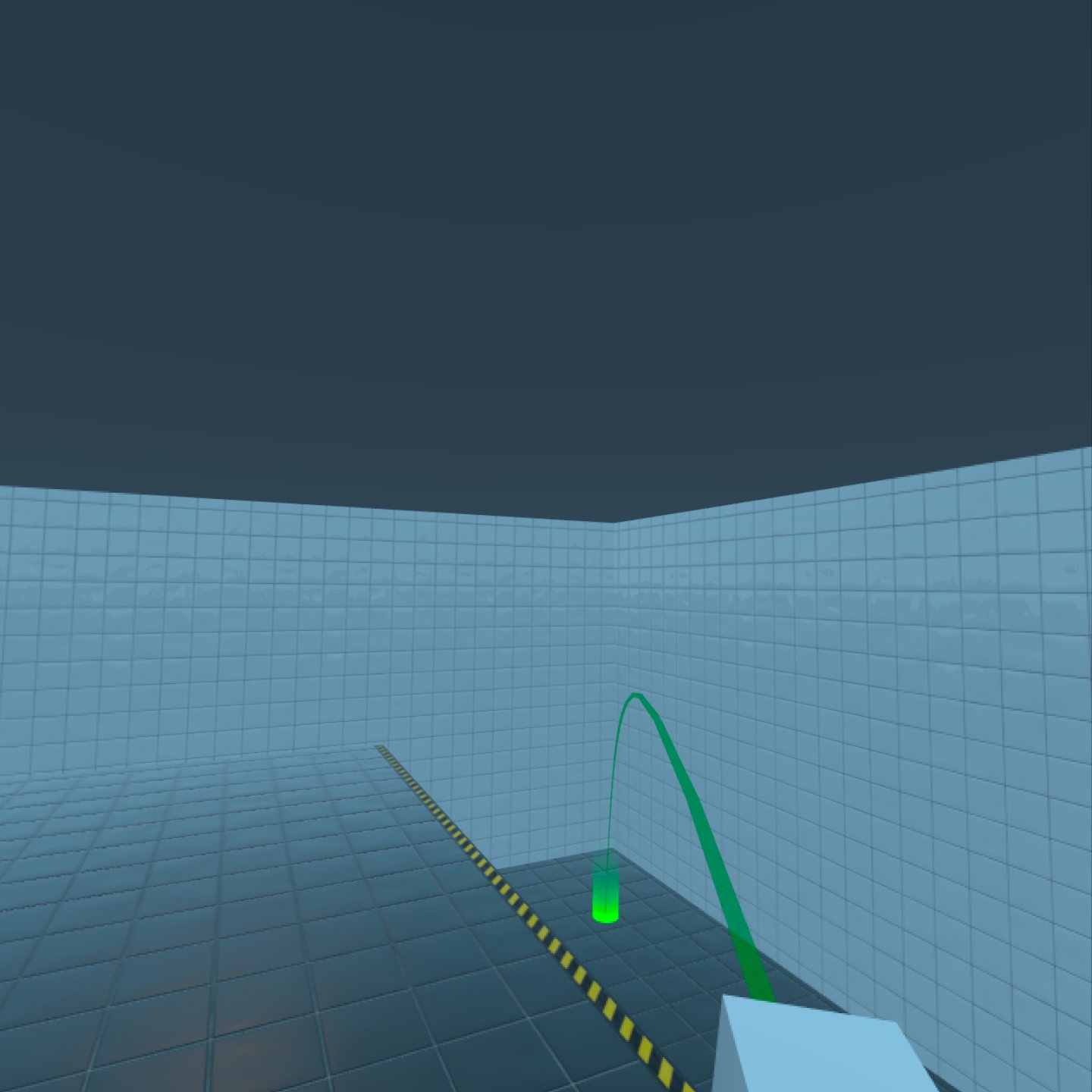
This example shows how to move to places in the virtual environment using a simple freeform teleportation system, a non-continuous form of movement.
When you run the example, use the following controls for navigation.
| 动作 | Control |
|---|---|
| Rotation | Left and Right stick on the right controller |
| Aim and Teleport | Forward stick on the right controller |
You can easily re-use
FreeformTeleporter
in other projects, as all the logic is contained within that type.
FreeformTeleporter { id: teleporter rayPicker: xrView cameraOrigin: xrOrigin camera: xrOrigin.camera beamHandle: xrRightController onDoTeleportation: (cameraOriginPosition)=> { xrOrigin.position = cameraOriginPosition } onDoRotation: (cameraOriginRotation, cameraOriginPosition)=> { xrOrigin.rotation = cameraOriginRotation xrOrigin.position = cameraOriginPosition } }
The FreeformTeleporter component has the following properties that need to be set:
var rayPicker
The
rayPicker
property can be any object that implements a rayPick method. In this example, we are using
XrView
's built-in ray-picking method.
Node cameraOrigin
The
cameraOrigin
property is the center of the camera's local reference space. In Xr this will be the location where tracked items, like the camera, will be placed relative to. We will, therefore, use the
XrOrigin
node as the cameraOrigin.
Node camera
The
camera
property contains the camera used to render the scene. In this example, we use the tracked
XrCamera
we created earlier.
Node beamHandle
The
beamHandle
property is the Node used as the teleportation beam's start point. In this example, we use the right controller
xrRightController
as the beamHandle.
另请参阅 Locomotion in Qt Quick 3D Xr .