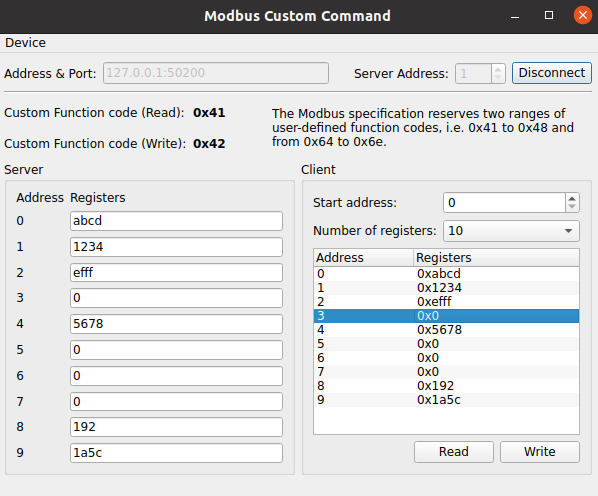
范例展示如何处理自定义 Modbus 功能代码。
The example acts as both Modbus client and server in a single application. The connection between them is established via Modbus TCP. It is used to send and receive custom Modbus requests and adjusts its internal states based on the request and response.
The main purpose of the example is to provide some demo code on how to implement a Modbus client or Modbus server handling custom Modbus function codes.
Modbus 协议支持功能代码范围
1 - 127 (0x01 - 0x7F HEX)
. Most of the function codes are well defined and publicly documented. However, there are two ranges that can be used for user-defined functions. Those are
65 - 72 (0x41 - 48 HEX)
and
100 - 110 (0x64 - 0x6E HEX)
. The user can select function codes from these ranges and handle them in some custom way.
此应用程序使用功能代码
65 (0x41 HEX)
以实现
CustomRead
命令和功能代码
66 (0x42 HEX)
以实现
CustomWrite
command. In this example the custom commands are used to simply read and write the
保持寄存器
.
自定义 Modbus 命令的发送是使用 QModbusClient::sendRawRequest () method. This method requires to generate a QModbusRequest object with the desired function code and a list of arguments which will be encoded into a QByteArray :
QModbusDataUnit unit {
QModbusDataUnit::HoldingRegisters,
ui->startAddress->value(),
qMin(ui->numberOfRegisters->currentText().toUShort(),
quint16(10 - ui->startAddress->value())) // do not go beyond 10 entries
};
for (qsizetype i = 0, total = unit.valueCount(); i < total; ++i)
unit.setValue(i, m_model->m_registers[i + unit.startAddress()]);
const quint8 byteCount = quint8(unit.valueCount() * 2);
QModbusRequest writeRequest {
QModbusPdu::FunctionCode(ModbusClient::CustomWrite),
quint16(unit.startAddress()),
quint16(unit.valueCount()), byteCount, unit.values()
};
The QModbusClient::sendRawRequest () 方法返回 QModbusReply object which can be used to check for errors as usual:
if (auto *reply = m_client.sendRawRequest(writeRequest, ui->serverAddress->value())) {
if (!reply->isFinished()) {
connect(reply, &QModbusReply::finished, this, [this, reply]() {
if (reply->error() == QModbusDevice::ProtocolError) {
statusBar()->showMessage(tr("Write response error: %1 (Modbus exception: 0x%2)")
.arg(reply->errorString()).arg(reply->rawResult().exceptionCode(), -1, 16),
5000);
} else if (reply->error() != QModbusDevice::NoError) {
statusBar()->showMessage(tr("Write response error: %1 (code: 0x%2)").
arg(reply->errorString()).arg(reply->error(), -1, 16), 5000);
}
reply->deleteLater();
}
);
}
} else {
statusBar()->showMessage(tr("Write error: ") + m_client.errorString(), 5000);
}
自定义服务器派生自 QModbusTcpServer 类。它覆写 QModbusServer::processPrivateRequest () 方法。
class ModbusServer : public QModbusTcpServer { Q_OBJECT Q_DISABLE_COPY_MOVE(ModbusServer) public: ModbusServer(QObject *parent = nullptr); private: QModbusResponse processPrivateRequest(const QModbusPdu &request) override; };
The base server class calls the processPrivateRequest () method when a command with a custom function code is received.
The custom implementation handles the
CustomRead
command by generating a
QModbusResponse
with the values of requested registers:
if (ModbusClient::CustomRead == request.functionCode()) {
quint16 startAddress, count;
request.decodeData(&startAddress, &count);
QModbusDataUnit unit(QModbusDataUnit::HoldingRegisters, startAddress, count);
if (!data(&unit)) {
return QModbusExceptionResponse(request.functionCode(),
QModbusExceptionResponse::IllegalDataAddress);
}
return QModbusResponse(request.functionCode(), startAddress, quint8(count * 2), unit.values());
}
Handling
CustomWrite
command includes extracting the new values from the received
QModbusPdu
, doing the actual value update, and returning a
QModbusResponse
with the registers that were actually updated:
if (ModbusClient::CustomWrite == request.functionCode()) {
quint8 byteCount;
quint16 startAddress, numberOfRegisters;
request.decodeData(&startAddress, &numberOfRegisters, &byteCount);
if (byteCount % 2 != 0) {
return QModbusExceptionResponse(request.functionCode(),
QModbusExceptionResponse::IllegalDataValue);
}
const QByteArray pduData = request.data().remove(0, WriteHeaderSize);
QDataStream stream(pduData);
QList<quint16> values;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRegisters; i++) {
quint16 tmp;
stream >> tmp;
values.append(tmp);
}
if (!writeData({QModbusDataUnit::HoldingRegisters, startAddress, values})) {
return QModbusExceptionResponse(request.functionCode(),
QModbusExceptionResponse::ServerDeviceFailure);
}
return QModbusResponse(request.functionCode(), startAddress, numberOfRegisters);
}
自定义客户端派生自 QModbusTcpClient 类。它覆写 QModbusClient::processPrivateResponse () 方法。
class ModbusClient : public QModbusTcpClient { Q_OBJECT Q_DISABLE_COPY_MOVE(ModbusClient) public: ModbusClient(QObject *parent = nullptr); static constexpr QModbusPdu::FunctionCode CustomRead {QModbusPdu::FunctionCode(0x41)}; static constexpr QModbusPdu::FunctionCode CustomWrite {QModbusPdu::FunctionCode(0x42)}; private: bool processPrivateResponse(const QModbusResponse &response, QModbusDataUnit *data) override; };
基客户端类调用 processPrivateResponse () method to process the server responses with custom function codes.
The custom implementation handles the responses with
CustomRead
and
CustomWrite
函数代码:
bool ModbusClient::processPrivateResponse(const QModbusResponse &response, QModbusDataUnit *data) { if (!response.isValid()) return QModbusClient::processPrivateResponse(response, data); if (CustomRead == response.functionCode()) return collateBytes(response, data); if (CustomWrite == response.functionCode()) return collateMultipleValues(response, data); return QModbusClient::processPrivateResponse(response, data); }
The
CustomRead
response is handled by decoding the provided
QModbusPdu
and extracting the values for requested registers:
static bool collateBytes(const QModbusPdu &response, QModbusDataUnit *data) { if (response.dataSize() < MinimumReadResponseSize) return false; quint16 address; quint8 byteCount; response.decodeData(&address, &byteCount); if (byteCount % 2 != 0) return false; if (data) { QDataStream stream(response.data().remove(0, 3)); QList<quint16> values; const quint8 itemCount = byteCount / 2; for (int i = 0; i < itemCount; i++) { quint16 tmp; stream >> tmp; values.append(tmp); } *data = {QModbusDataUnit::HoldingRegisters, address, values}; } return true; }
The
CustomWrite
response is handled by simply validating the response parameters:
static bool collateMultipleValues(const QModbusPdu &response, QModbusDataUnit *data) { if (response.dataSize() != WriteResponseSize) return false; quint16 address, count; response.decodeData(&address, &count); if (count < 1 || count > 10) return false; if (data) *data = {QModbusDataUnit::HoldingRegisters, address, count}; return true; }
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
This example cannot be used in conjunction with other applications. Once the example is started, it can only exchange custom Modbus commands within the application itself. All interactions between the client and server use the Modbus TCP protocol.