A Qt Quick app designed for landscape and portrait devices that uses custom components, responsive layouts, and JavaScript for the application logic.
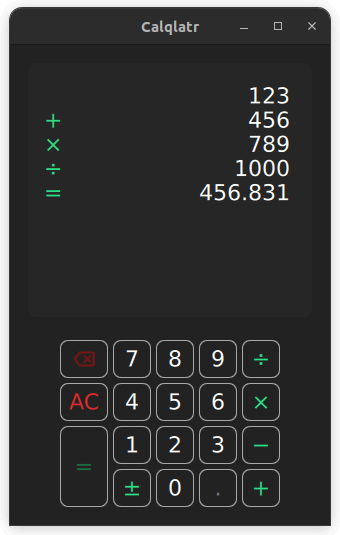
Calqlatr demonstrates various QML and Qt Quick features, such as displaying custom components and using responsive layouts. The application logic is implemented in JavaScript and the UI is implemented in QML.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
在 Calqlatr application, custom types are used. These are defined in their own separate .qml file:
To use these custom types in
Main.qml
, add an import statement for the
content
folder where the types are located:
import "content"
例如,
NumberPad
类型用于
Main.qml
to create the number pad of the calculator. This is nested within an
Item
type, the base type for all visual items in Qt Quick:
NumberPad {
id: numberPad;
Layout.margins: root.margin
}
Custom components are QML types that can be defined in any QML file, they behave the same as the components that are defined in their own .qml file, like
NumberPad.qml
。在
NumberPad.qml
the
DigitButton
component and the
OperatorButton
component are defined. New properties can be added or exsisting properties can be modified in these components. Here the
onReleased
handler is overwritten for both of the custom components.
component DigitButton: CalculatorButton {
onReleased: {
root.digitPressed(text)
updateDimmed()
}
}
component OperatorButton: CalculatorButton {
onReleased: {
root.operatorPressed(text)
updateDimmed()
}
textColor: controller.qtGreenColor
implicitWidth: 48
dimmable: true
}
In addition, use the
CalculatorButton
type for the different buttons on
NumberPad
.
CalculatorButton.qml
defines basic properties of a button, which you modify for each instance in
NumberPad.qml
. For the digit and operator buttons, a few extra properties are added, such as the
text
,
width
,和
dimmable
properties. Use
dimmable
to visually disable (dimmed) buttons whenever the calculator engine does not accept input from that button.
DigitButton {
text: "e"
dimmable: true
implicitWidth: 48
}
There is another file in the
content
directory called
BackSpaceButton.qml
, this is a special case of the
CalculatorButton
where we would like to render an image onto the button, rather than use text. This button is the same as an
OperatorButton
, but includes an
icon
而不是
text
:
icon.source: getIcon()
icon.width: 38
icon.height: 38
icon.color: getIconColor()
// include this text property as the calculator engine
// differentiates buttons through text. The text is never drawn.
text: "bs"
property bool dimmable: true
property bool dimmed: false
readonly property color backgroundColor: "#222222"
readonly property color borderColor: "#A9A9A9"
readonly property color backspaceRedColor: "#DE2C2C"
readonly property int buttonRadius: 8
function getBackgroundColor() {
if (button.dimmable && button.dimmed)
return backgroundColor
if (button.pressed)
return backspaceRedColor
return backgroundColor
In this example, responsive layouts arrange the different UI components for both portrait and landscape modes. It also lets you toggle between these two modes. You can notice this in
Main.qml
, which defines a
ColumnLayout
for portrait mode, and
RowLayout
for landscape.
ColumnLayout {
id: portraitMode
anchors.fill: parent
visible: true
LayoutItemProxy {
target: display
Layout.minimumHeight: display.minHeight
}
LayoutItemProxy {
target: numberPad
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignHCenter
}
}
RowLayout {
id: landscapeMode
anchors.fill: parent
visible: false
LayoutItemProxy {
target: display
}
LayoutItemProxy {
target: numberPad
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignVCenter
}
}
The
ColumnLayout
, represents the portrait layout for the application, and the
RowLayout
represents the landscape layout. The
visible
property handles which layout is used at a given time. The
id
特性为
NumberPad
and
显示
components are used to set the
target
特性为
LayoutItemProxy
types. This allows both layouts to use the same content items. In addition, properties can be forwarded within the
LayoutItemProxy
item to the
target
itself. For example, when the
NumberPad
is instantiated, both layouts require a different
Layout.alignment
.
Toggling between the two layouts is done in the signal handler for the
isPortraitMode
property, by setting their visibilities:
onIsPortraitModeChanged: {
if (isPortraitMode) {
portraitMode.visible = true
landscapeMode.visible = false
} else {
portraitMode.visible = false
landscapeMode.visible = true
}
}
This is possible because QML creates signal handlers for all self-declared properties, in this case the
on<Property>Changed
handler, where <property> is the
isPortraitMode
特性。
A responsive layout is also used in
NumberPad.qml
when defining the portrait and landscape layout for the
NumberPad
本身。
RowLayout {
spacing: controller.spacing
GridLayout {
id: scientificGrid
columns: 3
columnSpacing: controller.spacing
rowSpacing: controller.spacing
visible: !isPortraitMode
OperatorButton { text: "x²" }
OperatorButton { text: "⅟x" }
OperatorButton { text: "√" }
OperatorButton { text: "x³" }
OperatorButton { text: "sin" }
OperatorButton { text: "|x|" }
OperatorButton { text: "log" }
OperatorButton { text: "cos" }
DigitButton {
text: "e"
dimmable: true
implicitWidth: 48
}
OperatorButton { text: "ln" }
OperatorButton { text: "tan" }
DigitButton {
text: "π"
dimmable: true
implicitWidth: 48
}
}
GridLayout {
id: mainGrid
columns: 5
columnSpacing: controller.spacing
rowSpacing: controller.spacing
BackspaceButton {}
DigitButton { text: "7" }
DigitButton { text: "8" }
DigitButton { text: "9" }
OperatorButton {
text: "÷"
implicitWidth: 38
}
OperatorButton {
text: "AC"
textColor: controller.backspaceRedColor
accentColor: controller.backspaceRedColor
}
DigitButton { text: "4" }
DigitButton { text: "5" }
DigitButton { text: "6" }
OperatorButton {
text: "×"
implicitWidth: 38
}
OperatorButton {
text: "="
implicitHeight: 81
Layout.rowSpan: 2
}
DigitButton { text: "1" }
DigitButton { text: "2" }
DigitButton { text: "3" }
OperatorButton {
text: "−"
implicitWidth: 38
}
OperatorButton {
text: "±"
implicitWidth: 38
}
DigitButton { text: "0" }
DigitButton {
text: "."
dimmable: true
}
OperatorButton {
text: "+"
implicitWidth: 38
}
}
} // RowLayout
In this case, two
LayoutItemProxy
items are created. Their
target
properties are set to
scientificGrid
,
Grid
type, containing all the scientific buttons, and the
mainGrid
, another
Grid
type, containing all the standard buttons.
在
CalculatorButton.qml
, the text colors of the number pad buttons are also animated.
...
color: getBackgroundColor()
border.color: getBorderColor()
}
contentItem: Text {
text: button.text
font.pixelSize: button.fontSize
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
color: getTextColor()
Behavior on color {
ColorAnimation {
duration: 120
easing.type: Easing.OutElastic
}
The color changes are animated by defining a
行为
在
color
property. When a button is set to
dimmed = true
, the button appears darker. When a button is pressed, it lights up green. In order to dynamically change the
dimmed
property of all the buttons on the
NumberPad
,
buttonPressed
signal calls the
NumberPad
's
updateDimmed()
函数。
function updateDimmed(){
for (let i = 0; i < mainGrid.children.length; i++){
mainGrid.children[i].dimmed = root.isButtonDisabled(mainGrid.children[i].text)
}
for (let j = 0; j < scientificGrid.children.length; j++){
scientificGrid.children[j].dimmed = root.isButtonDisabled(scientificGrid.children[j].text)
}
}
The calculator.js file defines the calculator's engine. It contains variables to store the calculator's state, and functions that are called when the user presses the digit and operator buttons. To use the engine, import calculator.js into the
Main.qml
file using the alias
CalcEngine
:
import "content/calculator.js" as CalcEngine
By default, importing a JavaScript file from QML creates a new instance of it, and any state it contains is unique to that instance. The use of
.pragma library
allows the state to be shared amongst all users of the script.
.pragma library
When users press a digit, the text from the digit appears on the display. When they press an operator, the appropriate calculation is performed, and the result can be displayed using the equals (=) operator. The all-clear (AC) operator resets the calculator engine.
另请参阅 QML 应用程序 .