This example contains a QML project that you can import into Android Studio with the Qt Tools for Android Studio plugin and Java and Kotlin projects that utilize the QtQuickView API.
For more information on how QML works, see the Qt Qml . This documentation will focus on how a QML component is embedded into Java- and Kotlin-based Android applications.
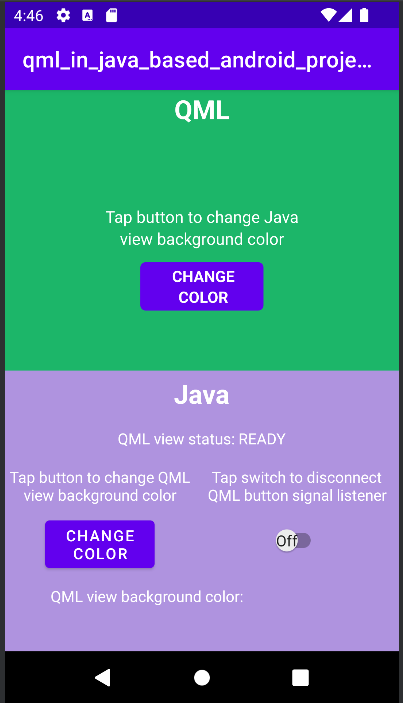
First, we look at the
MainActivity
's onCreate() method of the Java and Kotlin projects.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
m_mainLinear = findViewById(R.id.mainLinear);
m_getPropertyValueText = findViewById(R.id.getPropertyValueText);
m_qmlStatus = findViewById(R.id.qmlStatus);
m_androidControlsLayout = findViewById(R.id.javaLinear);
m_box = findViewById(R.id.box);
m_switch = findViewById(R.id.switch1);
m_switch.setOnClickListener(view -> switchListener());
m_qmlView = new QtQuickView(this, "qrc:/qt/qml/qml_in_android_view/main.qml",
"qml_in_android_view");
// Set status change listener for m_qmlView
// listener implemented below in OnStatusChanged
m_qmlView.setStatusChangeListener(this);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
m_qmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.qmlFrame);
m_qmlFrameLayout.addView(m_qmlView, params);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(view -> onClickListener());
// Check target device orientation on launch
handleOrientationChanges();
}
For a Kotlin-based project:
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
m_binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
val view = m_binding.root
setContentView(view)
m_binding.signalSwitch.setOnClickListener { switchListener() }
m_qmlView = QtQuickView(
this, "qrc:/qt/qml/qml_in_android_view/main.qml",
"qml_in_android_view"
)
// Set status change listener for m_qmlView
// listener implemented below in OnStatusChanged
m_qmlView!!.setStatusChangeListener(this)
val params: ViewGroup.LayoutParams = FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
m_binding.qmlFrame.addView(m_qmlView, params)
m_binding.changeColorButton.setOnClickListener { onClickListener() }
// Check target device orientation on launch
handleOrientationChanges()
}
注意: in the Kotlin project we use View binding to access the UI components of the application:
m_binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) val view = m_binding.root setContentView(view)
Inside the
onCreate()
method, an instance of
QtQuickView
命名
m_qmlView
is created by giving it the Java/Kotlin application Context, URI of the QML project's
main.qml
file and the name of the QML project's main library as parameters.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
m_qmlView = new QtQuickView(this, "qrc:/qt/qml/qml_in_android_view/main.qml",
"qml_in_android_view");
For a Kotlin-based project:
m_qmlView = QtQuickView(
this, "qrc:/qt/qml/qml_in_android_view/main.qml",
"qml_in_android_view"
)
m_qmlView
is then added to Android FrameLayout ViewGroup with appropriate layout parameters.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
m_qmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.qmlFrame);
m_qmlFrameLayout.addView(m_qmlView, params);
For a Kotlin-based project:
val params: ViewGroup.LayoutParams = FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
m_binding.qmlFrame.addView(m_qmlView, params)
To interact with the embedded QML component we first need to implement the QtQuickView public interface StatusChangeListener .
对于基于 Java 的工程:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements QtQuickView.StatusChangeListener{ ... }
IFor a Kotlin-based project:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), QtQuickView.StatusChangeListener{ ... }
Then, define an override for the
StatusChangeListener
callback function
onStatusChanged()
.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
@Override
public void onStatusChanged(int status) {
Log.i(TAG, "Status of QtQuickView: " + status);
final String qmlStatus = getResources().getString(R.string.qml_view_status)
+ m_statusNames.get(status);
// Show current QML View status in a textview
m_qmlStatus.setText(qmlStatus);
// Connect signal listener to "onClicked" signal from main.qml
// addSignalListener returns int which can be used later to identify the listener
if (status == QtQuickView.STATUS_READY && !m_switch.isChecked()) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_qmlView.connectSignalListener("onClicked", Object.class,
(String signal, Object o) -> {
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked");
m_androidControlsLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(m_colors.getColor()));
});
}
}
For a Kotlin-based project:
override fun onStatusChanged(status: Int) {
Log.v(TAG, "Status of QtQuickView: $status")
val qmlStatus = (resources.getString(R.string.qml_view_status)
+ m_statusNames[status])
// Show current QML View status in a textview
m_binding.qmlStatus.text = qmlStatus
// Connect signal listener to "onClicked" signal from main.qml
// addSignalListener returns int which can be used later to identify the listener
if (status == QtQuickView.STATUS_READY && !m_binding.signalSwitch.isChecked) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_qmlView!!.connectSignalListener(
"onClicked", Any::class.java
) { _: String?, _: Any? ->
Log.v(TAG, "QML button clicked")
m_binding.kotlinLinear.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(m_colors.getColor()))
}
}
}
Then, set that listener to listen for status changes of
m_qmlView
采用
setStatusChangeListener()
.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
m_qmlView.setStatusChangeListener(this);
For a Kotlin-based project:
m_qmlView!!.setStatusChangeListener(this)
The overridden callback function
onStatusChanged()
receives
StatusChanged()
signal containing the current
Status value
的
m_qmlView
. If this
Status value
is confirmed to be
STATUS_READY
, we can start interacting with the QML view.
Getting and setting QML view property values happens through the QtQuickView.getProperty() and QtQuickView.setProperty() 方法。
The root object of the QML component's background color is set when a click event of an Android button occurs.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
public void onClickListener() {
// Set the QML view root object property "colorStringFormat" value to
// color from Colors.getColor()
m_qmlView.setProperty("colorStringFormat", m_colors.getColor());
String qmlBackgroundColor = m_qmlView.getProperty("colorStringFormat");
// Display the QML View background color code
m_getPropertyValueText.setText(qmlBackgroundColor);
// Display the QML View background color in a view
m_box.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(qmlBackgroundColor));
}
For a Kotlin-based project:
private fun onClickListener() {
// Set the QML view root object property "colorStringFormat" value to
// color from Colors.getColor()
m_qmlView!!.setProperty("colorStringFormat", m_colors.getColor())
val qmlBackgroundColor = m_qmlView!!.getProperty<String>("colorStringFormat")
// Display the QML View background color code
m_binding.getPropertyValueText.text = qmlBackgroundColor
// Display the QML View background color in a view
m_binding.colorBox.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(qmlBackgroundColor))
}
With the QtQuickView.setProperty() method we set the "colorStringFormat" property value to a random color value that is fetched from the project's
Colors.java
类。
The QtQuickView.getProperty() {QtQuickView.getProperty()} method is used here to fetch the current background color of the root object of the QML component and then show it to the user on the Android side of the application.
QtQuickView class offers a connectSignalListener() and disconnectSignalListener() methods which are used to connect and disconnect a signal listener to a signal that is declared in the QML component root object.
Here we connect a signal listener to the
onClicked()
signal of the QML component.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
if (status == QtQuickView.STATUS_READY && !m_switch.isChecked()) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_qmlView.connectSignalListener("onClicked", Object.class,
(String signal, Object o) -> {
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked");
m_androidControlsLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(m_colors.getColor()));
});
}
For a Kotlin-based project:
if (status == QtQuickView.STATUS_READY && !m_binding.signalSwitch.isChecked) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_qmlView!!.connectSignalListener(
"onClicked", Any::class.java
) { _: String?, _: Any? ->
Log.v(TAG, "QML button clicked")
m_binding.kotlinLinear.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(m_colors.getColor()))
}
}
The
onClicked()
signal is emitted every time the button on the QML UI is clicked. That signal is then received by this listener and the background color of the layout holding the Android side of the application is set to a random color value fetched from the project's
Colors.java
类。
The QtQuickView.connectSignalListener() returns a unique signal listener id which we store and use later to identify and disconnect the listener.
对于基于 Java 的工程:
m_qmlView.disconnectSignalListener(m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId);
For a Kotlin-based project:
m_qmlView!!.disconnectSignalListener(m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId)
Here, the previously connected signal listener is disconnected using the QtQuickView.disconnectSignalListener() method by giving it the unique signal listener id.