展示如何使用各種特徵的 QSerialPort .
終端 展示如何為簡單串行接口創建終端使用 Qt Serial Port .
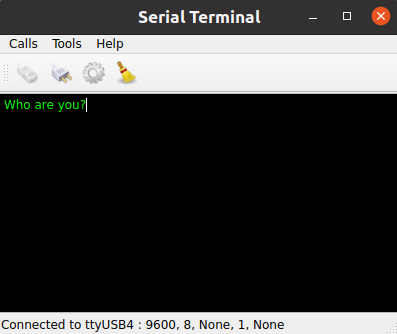
This example shows the main features of the QSerialPort class, like configuration, I/O implementation and so forth. Also, the class QSerialPortInfo is invoked to display information about the serial ports available in the system.
QSerialPort 支持 2 種常規編程方式:
waitFor...()
functions can be called (i.e.
QSerialPort::waitForReadyRead
()) to suspend the calling thread until the operation has completed.
In this example, the asynchronous approach is demonstrated. The Blocking Receiver example illustrates the synchronous approach.
我們的範例包含一些 GUI 小部件:
MainWindow
(
terminal/mainwindow.cpp
) - is the main application window that contains all the working logic for the serial port programming, including configuration, I/O processing and so forth, while inheriting the QMainWindow.
Console
(
terminal/console.cpp
) - is the central widget of the main window, displaying the transmitted or received data. The widget is derived from the QPlainTextEdit class.
SettingsDialog
(
terminal/settingsdialog.cpp
) - is a dialog for configuring the serial port, as well as for displaying the available serial ports and information about them.
串口被實例化在
MainWindow
constructor. The main widget is passed as the parent, so the object deletion happens automatically according to the parent and child mechanism in Qt:
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : QMainWindow(parent), m_ui(new Ui::MainWindow), m_serial(new QSerialPort(this)) { ...
This example demonstrates the following QSerialPort signals:
...
connect(m_serial, &QSerialPort::readyRead, this, &MainWindow::readData);
connect(m_serial, &QSerialPort::bytesWritten, this, &MainWindow::handleBytesWritten);
...
}
點擊
Connect
按鈕援引
openSerialPort()
槽:
void MainWindow::openSerialPort() { const SettingsDialog::Settings p = m_settings->settings(); m_serial->setPortName(p.name); m_serial->setBaudRate(p.baudRate); m_serial->setDataBits(p.dataBits); m_serial->setParity(p.parity); m_serial->setStopBits(p.stopBits); m_serial->setFlowControl(p.flowControl); if (m_serial->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite)) { m_console->setEnabled(true); m_console->setLocalEchoEnabled(p.localEchoEnabled); m_ui->actionConnect->setEnabled(false); m_ui->actionDisconnect->setEnabled(true); m_ui->actionConfigure->setEnabled(false); showStatusMessage(tr("Connected to %1 : %2, %3, %4, %5, %6") .arg(p.name, p.stringBaudRate, p.stringDataBits, p.stringParity, p.stringStopBits, p.stringFlowControl)); } else { QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("Error"), m_serial->errorString()); showStatusMessage(tr("Open error")); } }
In this slot, the settings are read from
SettingsDialog
and an attempt is made to open and initialize the serial port accordingly. If successful, the status bar displays a message that the opening was successful with the given configuration; otherwise, a messagebox is displayed with the appropriate error code and message. If the serial port settings have never been called then the terminal attempts to open the port with the default settings: 9600 8N1.
點擊
Disconnect
按鈕援引
closeSerialPort()
槽:
void MainWindow::closeSerialPort() { if (m_serial->isOpen()) m_serial->close(); m_console->setEnabled(false); m_ui->actionConnect->setEnabled(true); m_ui->actionDisconnect->setEnabled(false); m_ui->actionConfigure->setEnabled(true); showStatusMessage(tr("Disconnected")); }
In this case, handled by the closure of the serial port.
點擊
Configure
按鈕援引
show()
槽屬於
SettingsDialog
小部件。
此方法 (
terminal/settingsdialog.cpp
) 顯示
SettingsDialog
, in which the user can choose the desired serial port, see the information about the selected port, and set the desired parameters of the given serial port.
Typing characters in the console invokes the
writeData()
槽:
void MainWindow::writeData(const QByteArray &data) { const qint64 written = m_serial->write(data); if (written == data.size()) { m_bytesToWrite += written; m_timer->start(kWriteTimeout); } else { const QString error = tr("Failed to write all data to port %1.\n" "Error: %2").arg(m_serial->portName(), m_serial->errorString()); showWriteError(error); } }
This slot sends the characters typed in the given Console widget to the serial port - see
terminal/console.cpp
. It also starts a timer to track if the write actually succeeded or not. We use the
bytesWritten
() signal to make sure that all bytes are actually written. It is connected to the
MainWindow::handleBytesWritten()
槽:
void MainWindow::handleBytesWritten(qint64 bytes) { m_bytesToWrite -= bytes; if (m_bytesToWrite == 0) m_timer->stop(); }
When the serial port receives new data, the signal
readyRead
() is emitted, and that signal is connected to the
MainWindow::readData()
槽:
void MainWindow::readData() { const QByteArray data = m_serial->readAll(); m_console->putData(data); }
This slot reads the data from the serial port and displays that in the Console widget.
要運行範例從 Qt Creator ,打開 Welcome 模式,然後選擇範例從 Examples 。更多信息,拜訪 構建和運行範例 .
另請參閱 Blocking Receiver .